An inventory account (such as F.G. Inventory or Work-in-Process) is debited for $834; this is the standard cost of the direct materials component in the aprons manufactured in January 2023. See direct material total variance#Example and direct material price variance#Example for computations of both components. Watch this video featuring a professor of accounting walking through the steps involved in calculating a material price variance and a material quantity variance to learn more. The actual quantity used can differ from the standard quantity because of improved efficiencies in production, carelessness or inefficiencies in production, or poor estimation when creating the standard usage. In manufacturing, efficiency variance can be used to analyze the effectiveness of an operation with respect to labor, materials, machine time, and other production factors. Using the standard and actual data given for Lastlock and the direct labor variance template, compute the direct labor variances.
How is Efficiency Variance Calculated? – A Complete Guide to Efficiency Variance
Moreover, we will discuss the role of technology in reducing efficiency variance, common causes of efficiency variance, and best practices for addressing it in a manufacturing plant. Additionally, we will explore when a company should consider investing in new equipment, outsourcing specific processes, and how to ensure that employees are properly trained to minimize efficiency variance. Sometimes these flexible budget figures and overhead rates differ from the actual results, which produces a variance. It’s thus typical for management personnel to set expectations and benchmarks for both costs and output, while the manufacturing activity is still in its planning stage before the production process even starts.
- If the cost of maintaining and repairing current equipment is high, investing in new equipment may be more cost-effective in the long run.
- Labor yield variance arises when there is a variation in actual output from standard.
- Fixed manufacturing overhead is, by definition, fixed and should not change as long as production remains within the relevant range.
- Interpretation of the variable overhead rate variance is often difficult because the cost of one overhead item, such as indirect labor, could go up, but another overhead cost, such as indirect materials, could go down.
- This team of experts helps Finance Strategists maintain the highest level of accuracy and professionalism possible.
Total direct labor variance
Here are some ways that technology can be used to reduce efficiency variance in manufacturing. Poor production planning can result in inefficient use of resources, leading to increased costs and reduced efficiency. For example, if a production process is not scheduled correctly, it can result in delays, overtime, and increased costs.
Great! The Financial Professional Will Get Back To You Soon.
The production that is acceptable (not rejected products) and which is assigned manufacturing costs of direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. With either of these formulas, the actual quantity used refers to the actual amount of materials used to create one unit of product. Standard cost projections are established for the variable and fixed components of manufacturing overhead. Manufacturing overhead includes all costs incurred to manufacture a product that are not direct material or direct labor. Sales of Lastlock skyrocketed when a local celebrity posted about Lastlock on social media. While the sudden increase in sales demand was exciting, Patty was not expecting the sudden increase in production so she experienced a number of production issues.
The actual quantity purchased and used to produce 150,000 units was 600,000 feet of flat nylon cord costing $330,000. The actual price of $0.55 per unit is not given in the actual data presented in Exhibit 8-1. However, it can be calculated by taking the total purchase price and dividing it by the total number of feet purchased. Overhead variance is a type of efficiency variance that measures the difference between the actual overhead costs incurred during a given period and the overhead costs that were budgeted for that same period. This variance is calculated by subtracting the standard overhead costs from the actual overhead costs and multiplying the difference by the actual quantity produced.
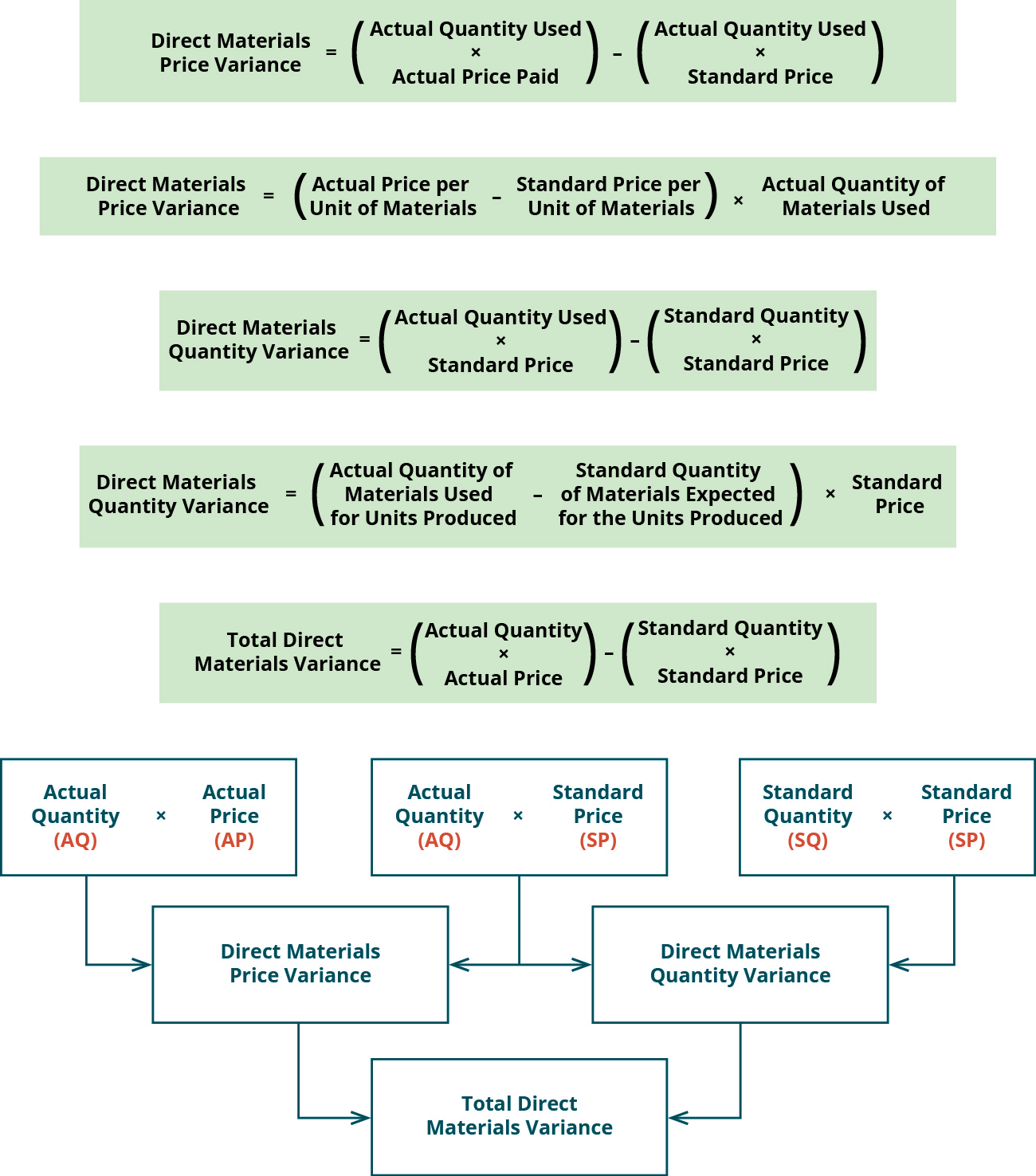
This result is interpreted as the organization paid $30,000 more for materials used in production than they planned. This direct materials price variance could indicate a purchasing issue, such as the purchasing department paying more than the agreed-upon amount (purchase order amount). Or the cause could be a supplier or sourcing issue in which sales returns and allowances recording returns in your books the material can be sourced cheaper elsewhere. Another possibility is that the direct material price standard needs to be increased because prices have increased. This variance is calculated by subtracting the standard quantity of materials from the actual quantity of materials and multiplying the difference by the standard price per unit.
Knowing that variable manufacturing costs were $181,500 over budget is helpful, but it doesn’t isolate the production issue or issues. Therefore, the next step is to individually analyze each component of variable manufacturing costs. The total variable manufacturing costs variance is separated into direct materials variances, direct labor variances, and variable manufacturing overhead variances. If the direct labor is not efficient when producing the good output, there will be an unfavorable labor efficiency variance.

Standards are cost or revenue targets used to make financial projections and evaluate performance. For example, if the cost formula for supplies is $3 per unit ($3Q), it is also considered the standard cost for supplies. Managers can use the standard cost formula to make projections about supplies expense or to evaluate the actual amount spent on supplies. Moreover, we have discussed the role of technology in reducing efficiency variance, common causes of efficiency variance, and best practices for addressing it in a manufacturing plant.
Companies that lack the financial resources to invest in new equipment or training programs may find it challenging to address this issue effectively. Outsourcing can be an excellent solution to ensure consistent quality and efficiency across all locations if a company operates in multiple locations or countries. A third-party provider with a global presence and expertise can help ensure that processes are performed consistently and efficiently across all locations. A comprehensive training program that covers all aspects of the manufacturing operation should be developed, including equipment operation, quality control, safety, and efficiency. The program should include both classroom and hands-on training to ensure that employees understand the concepts and can apply them in the workplace.
They are also responsible for monitoring efficiency variance and analyzing the data to identify areas for improvement. The quality control manager works closely with the production manager to ensure that production processes are optimized and that efficiency variance is minimized. Labor rate variance arises when labor is paid at a rate that differs from the standard wage rate. Labor efficiency variance arises when the actual hours worked vary from standard, resulting in a higher or lower standard time recorded for a given output. Materials price variance represents the difference between the standard cost of the actual quantity purchased and the actual cost of these materials. That part of a manufacturer’s inventory that is in the production process and has not yet been completed and transferred to the finished goods inventory.

